|
For some people, therapy is a big scary word. For some it is new age nonsense. For others, it is a sign of weakness. Many of our grandparents and parent went years not talking about what they felt and thought, they did not process their feelings and emotions, and as they say ‘they turned out just fine.’ But despite this thought process, there has been a rise in people who attend psychotherapy, particularly among more recent generations- millennials and Gen Z as the stigma regarding therapy in North America has significantly reduced.
0 Comments
If you’re thinking about giving therapy a try or looking for a therapist for your child, you might be understandably feeling a bit uncertain or nervous about getting started. You may have questions about what it might look like, whether you or your child are ready, how to find the right therapist, and more. Here is some information about therapy that can help you figure out if therapy is right for you or your child and how it might help.
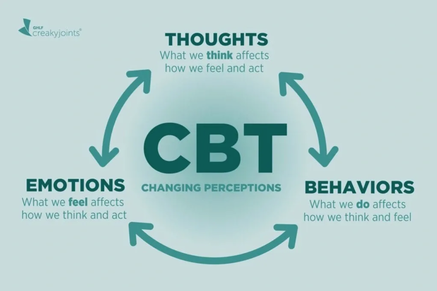
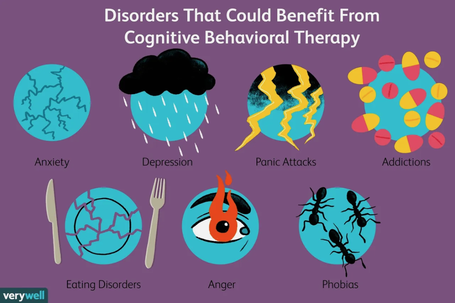
Tina Donvito (CreakyJoints Mental Health) CBT stands for Cognitive Behavioural Therapy which is a form of psychotherapy. Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy, is the practice of using psychological methods to help treat mental disorders [as opposed to using medical means]. Who Does CBT Help? Cognitive Behavioural Therapy helps people develop important skills and strategies to improve their mental health. Accordingly, this form of psychotherapy can help several people diagnosed with numerous different mental disorders. Some disorders for which CBT is commonly recommended include: · Bipolar Disorder · Eating Disorders [eg. anorexia nervosa] · Depression · Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) · Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) · Substance Use Disorders · Panic Disorders · Specific Phobias · And many more … How Does CBT Work? Like many other forms of therapy, the main goal for CBT is to improve a person’s health and to equip them with the proper techniques & strategies for them to maintain a healthy lifestyle. In particular, CBT treatment involves efforts to change one’s thinking and behavioural patterns (American Psychological Association). To do so, a therapist begins by discussing client problems with the client to determine underlying motivations. Then, a strategy is formed collaboratively to help re-shape the client’s thoughts, attitudes, and beliefs related to the client’s emotions & behaviours (CAMH). verywellmind Benefits of CBT CBT offers numerous benefits including: Developmental of Healthier Thought Patterns By discussing problems with a trained mental health professional, CBT helps clients become aware of their negative [typically unrealistic] thoughts. This awareness helps reduce future negative thoughts and feelings because the client can recognize when such thoughts are unfounded in reality. Effective Alternative to Medication However, it can also be combined with medication for a more holistic approach to treatment. Problem-Focused & Goal-Oriented CBT is individualized to a client to ensure their needs are best met by the therapist. Fast Results CBT is very structured to teach appropriate skills & strategies. As such, it is also time-limited to ensure results are aligning with the client’s current problems. Accessibility CBT is a widely recognized, evidence-based form of treatment for mental disorders. As such, there are numerous centres that offer CBT as treatment thus increasing access to this form of therapy. CBT is often significantly more affordable than other forms of therapy. CBT can be performed both virtually and in-person thus providing access to more individuals, including those in remote or underserviced areas. Three CBT TechniquesCognitive Behavioural Therapy involves a wide array of techniques. Here are 3 common ones you can try at home: 1. Problem-Solving In CBT, this skill is often broken down into 5 simpler steps to help ensure success. i. Step 1 – Identify the Problem ii. Step 2 – Create a List of Possible Solutions iii. Step 3 – Assess Pros & Cons of Each Solution iv. Step 4 – Select One Solution to Implement v. Step 5 – Apply the Chosen Solution to the Problem 2. Self-Monitoring Self-monitoring is an important CBT technique because it involves tracking one’s behaviours over time and then sharing them with one’s therapist. By keeping a record of one’s behaviours, thoughts, and symptoms, one can better provide relevant information to inform the treatment program. Thus, self-monitoring helps ensure the best possible treatment for one’s disorder. EG. For individuals with eating disorders, self-monitoring can include keeping track of eating habits [ie. what they eat & when] and one’s attitude during eating habits [ie. positive versus negative thoughts/feelings when eating] 3. Goal Setting Goal setting is a key step in recovery for mental illness because it provides a concrete desired result. CBT also commonly employs setting SMART goals, with SMART standing for specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-based. Such goals are important in CBT because they can demonstrate client progress. Try creating SMART goals for yourself! For more, check out Very Well Mind: https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-cognitive-behavior-therapy-2795747 Support If you are suffering from a mental health disorder and are considering CBT for treatment, consider booking a consultation with Inner Oak Therapy as the first step in your journey to better health! AuthorWritten by Gabrielle Bulman Thomas Social anxiety disorder is one of the most common forms of anxiety. The Anxiety Canada website suggests that between 7-13% of people are affected. It tends to emerge during interactions with others or during performance situations. Some common examples of anxiety-producing situations include public speaking or giving presentations, participating in a class or group discussion, eating in front of others, meeting new people, communicating with others, or attending social events.
SELF REGULATION AND EMOTIONAL DYSREGULATION
What do they mean and how are they, well…Everything? |
Archives
March 2023
Categories
All
|
- Home
- Who We Serve
- About
-
Services
- Child Therapy Burlington Ontario
- Adolescent Counselling Burlington Ontario
- Burlington Adult Therapy
- Parent Therapy Burlington Ontario
- Burlington Family Counselling
- Burlington Individual Therapy
- Couples Therapy Burlington
- Mental Health Therapy Burlington
- Burlington Anxiety Therapy
- Depression Therapy Burlington Ontario
- Burlington PTSD Counselling
- Burlington ADHD Therapy Services
- Borderline Personality Disorder Therapy Burlington
- Milton Psychotherapy Services
- Child Therapy Milton Ontario
- Adult Therapy Milton ON
- Milton Family Counselling
- Couples Therapy Milton Ontario
- Mental Health Therapy Milton
- Walk and Talk Therapy
- EMDR Therapy
- Contact
- Book Now
- Blog







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
